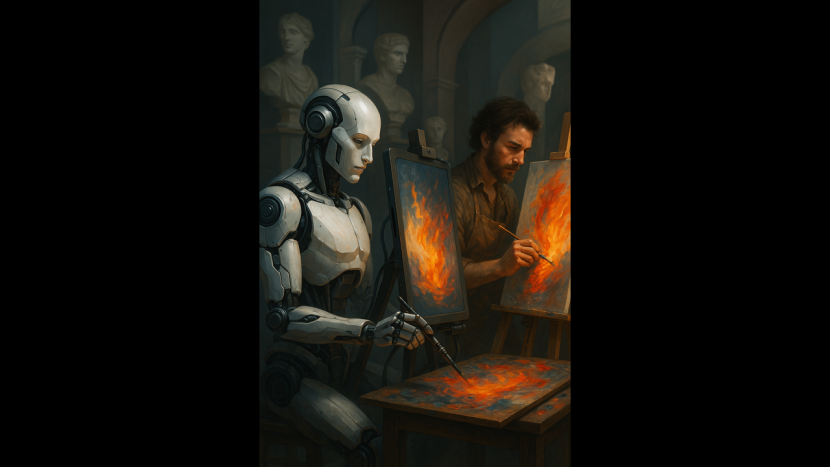
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly entered the world of creativity, blurring the lines between human imagination and machine-generated innovation. What was once thought to be exclusive to human intellect—painting, composing music, writing poetry—is now being tackled impressively by machines. AI is creating stunning visual art, generating original musical compositions, and even writing screenplays, often leaving audiences surprised at its technical skill and stylistic mimicry.
One AI-generated portrait, titled Edmond de Belamy, famously sold for over $400,000 at a Christie’s auction. AI systems like OpenAI’s MuseNet and Google’s Magenta are composing symphonies and jazz pieces that sound as though they came from human hands. These developments spark awe and curiosity—but also raise a critical question: Can artificial intelligence truly replicate—or even replace—the creativity that defines human artistry?
Fine arts have long been a deeply personal and emotional form of expression, reflecting the artist’s inner world, culture, and experiences. As AI becomes increasingly capable of producing artworks that mimic human aesthetics, the debate intensifies. Is AI a creative rival or simply a powerful tool? Can it ever match the soul behind a brushstroke or the feeling embedded in a melody? Let’s explore together.
Understanding Human Creativity in Art
Human creativity in art goes far beyond technical skill—it’s driven by emotion, intention, personal experience, and cultural context. Artists use art to express complex feelings and ideas, often shaped by their unique perspectives, histories, and inner worlds. Unlike AI, which lacks consciousness and emotion, humans create with purpose and meaning.
Spontaneity, intuition, and even imperfections play vital roles in the creative process, often leading to unexpectedly powerful results. Art reflects the human condition, making it deeply personal and emotionally resonant—something no algorithm can fully replicate.
How AI Creates Art
AI creates art by using advanced algorithms—particularly machine learning and neural networks—to analyze and replicate patterns from vast datasets of existing artworks. These systems are trained to understand styles, colors, composition, and forms, allowing them to generate original images, music, or text based on the data they’ve learned.
Tools like DALL·E, Midjourney, and Runway ML can produce paintings or visual art from simple text prompts, while AI music programs compose melodies in various genres. However, while the output may appear creative, AI lacks consciousness, emotion, or true understanding—its “creativity” is a product of pattern recognition, not inspiration or intention.
Strengths of AI in Fine Arts
AI brings several advantages to the world of fine arts. It can generate art quickly and in large volumes, saving time for artists and designers. AI can also blend styles, mimic famous artists, and explore endless creative possibilities by processing vast datasets far beyond human capacity.
These tools can help artists brainstorm, experiment with new styles, or visualize concepts that might be difficult to create manually. Additionally, AI democratizes art by making creative tools accessible to non-artists, empowering more people to express themselves visually or musically.
While it may not feel emotion, AI excels in speed, efficiency, and innovation—making it a valuable collaborator in the creative process.
Limitations of AI-Generated Art
Despite its capabilities, AI-generated art lacks genuine emotion, intention, and personal experience—core elements that give human art its depth and meaning. AI doesn’t feel, reflect, or understand; it simply mimics patterns from data it has been trained on.
There’s also the issue of originality. Since AI relies on existing works to create new ones, its output can feel derivative or lacking in true innovation. Ethical concerns arise too, such as copyright, authorship, and the authenticity of machine-made creations.
Ultimately, AI can produce visually impressive art, but it struggles to capture the soul and story that make human creativity truly powerful.
Human + AI: A Creative Collaboration
Rather than replacing artists, AI is increasingly seen as a tool that can enhance human creativity. Artists are using AI to experiment with new styles, automate repetitive tasks, and generate fresh ideas that might not arise through traditional methods alone.
This collaboration allows humans to focus on emotional depth, storytelling, and intention, while AI contributes speed, precision, and pattern recognition. Together, they can push the boundaries of what’s creatively possible, blending human imagination with machine efficiency.
When used thoughtfully, AI becomes a powerful partner—not a rival—in the artistic process.
The Future of Creativity
As AI continues to evolve, it will play a growing role in the creative industries—but not as a replacement for human artists. The future of creativity lies in a balanced partnership, where technology enhances rather than imitates human expression.
We may see new art forms emerge from this collaboration, combining machine precision with human emotion and context. However, the essence of true creativity—storytelling, meaning, and emotional depth—will remain rooted in the human experience.
In the end, AI may reshape how we create, but the soul of art will still belong to the human spirit.
Final Thoughts
The rise of AI in fine arts has sparked both excitement and concern—challenging traditional ideas about creativity and artistic value. While AI can generate impressive works and serve as a powerful creative tool, it lacks the emotional depth, intuition, and lived experience that define human art.
Rather than fearing replacement, artists can embrace AI as a collaborator that enhances the creative process. By combining human imagination with machine intelligence, we open the door to new possibilities in art and expression.
Ultimately, creativity is not just about producing something beautiful—it’s about conveying meaning, connecting with others, and reflecting the human condition. And that is something no machine can truly replicate.